SM2 Algorithm Principle
SM2 algorithm is a national secret standard asymmetric algorithm, designed based on elliptic curve cryptography (ECC). Unlike RSA, which is based on the difficulty of factoring large integers, the security of SM2 is based on the elliptic curve discrete logarithm problem. If you need to understand RSA, you can refer to (RSA Algorithm Understanding).
SM2 Elliptic Curve
The elliptic curve equation used by SM2 is:
What does the elliptic curve look like? Seeing is believing, and pictures can give you a direct feeling.
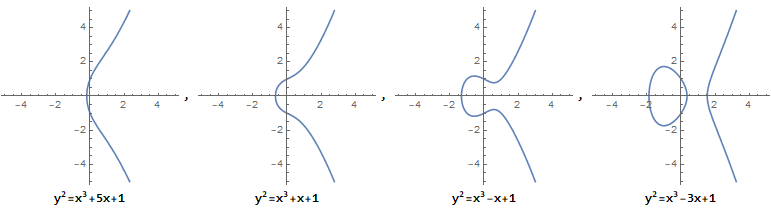
Why does
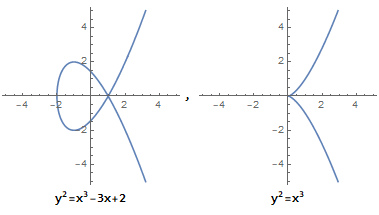
SM2 public and private keys
SM2 key pair generation is based on point operations on elliptic curves. The main steps are as follows:
- Select the elliptic curve parameters (a, b) and the base point G
- Randomly generate a private key d (a large integer)
- Calculate the public key Q = dG (d times G)
TIP
The private key is a large integer, and the public key is a point on the curve (including x and y coordinates)
Combined with the following picture, let's understand the geometric meaning of SM2 and what point doubling operation is.
- First choose an elliptic curve, that is, the values of a and b in the fixed formula
, assuming that the curve shown in the figure above is selected. - Randomly select a point P as the base point, make a tangent to the curve, pass through point Q, and tangent point R1.
- Based on the x-axis, make R the symmetric point of R1, then SM2 defines addition as P + Q = R, which is elliptic curve addition.
- Find the 2-fold point. When P = Q, that is, P + P = R = 2P, then R is the 2-fold point of P.
- Find the 3-fold point. 3P = P + 2P = P + R. Make a straight line through P and R, intersecting at the elliptic curve point M1. The symmetric point M based on the x-axis is the 3-fold point, and so on.
- Find the d-fold point. Assume that we have the same number of times d and the operation of the fold point is Q.
- d is the private key and Q is the public key. So the private key is a large integer and the public key is a point coordinate.
The above geometric reasoning is for easy understanding. The actual values are all on the prime finite field. After reasoning and calculation, cryptography experts have selected the optimal elliptic curve on the prime finite field for us. Unless there is a special need, there is no need to customize the curve.
SM2 recommended curves

p: the set of points of the elliptic curve on the finite field Fp of prime number p;
a: the value of the elliptic curve parameter a;
b: the value of the elliptic curve parameter b;
n: the value range, the value range of the random integer d
; Gx: the x coordinate value of the base point, similar to the x coordinate value of point P;
Gy: the y coordinate value of the base point, similar to the y coordinate value of point P.
SM2 encryption
The length of the SM2 encryption result is predictable: for a plaintext of length n bytes, the encrypted ciphertext length is
Encryption process:
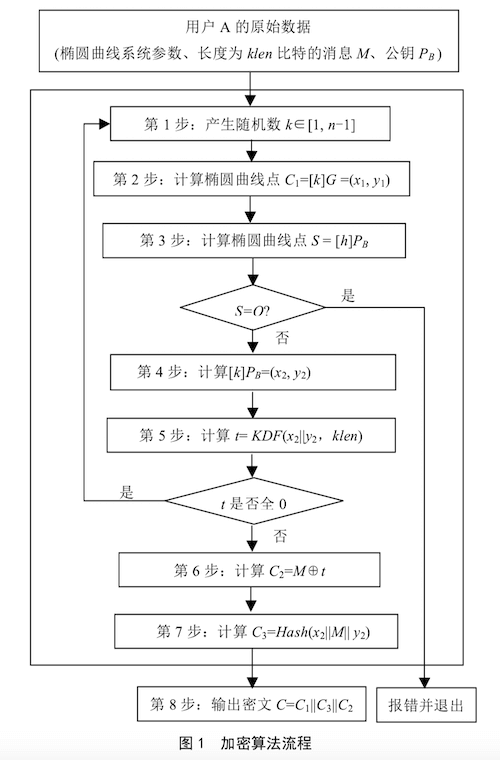
Let the elliptic curve be the recommended curve, the public key Q, the original text bit string M, and klen be the bit length of M;
- Calculate the random elliptic curve point
, k is a random number, G is the base point, and the calculated multiple point C1 is 64 bytes; - Verify the public key Q, calculate the elliptic curve point
, h is the cofactor, if S is an infinite point, exit; - Calculate the elliptic curve point
, and obtain x2, y2; - Calculate
, if t is a full 0 bit string, return to step 1, KDF is the key derivation function of SM2; - Calculate
, encrypt the plaintext, C2 is the real ciphertext, the length is the same as the original text; - Calculate
, generate a hash value, used to verify the data, the length is 32 bytes; - Output the ciphertext
, C is the ciphertext result.
Note
- The implementation of OpenSSL uses ASN.1 encoding, so the ciphertext length may not be fixed
- Due to the use of random numbers, the encryption results are different each time
SM2 decryption
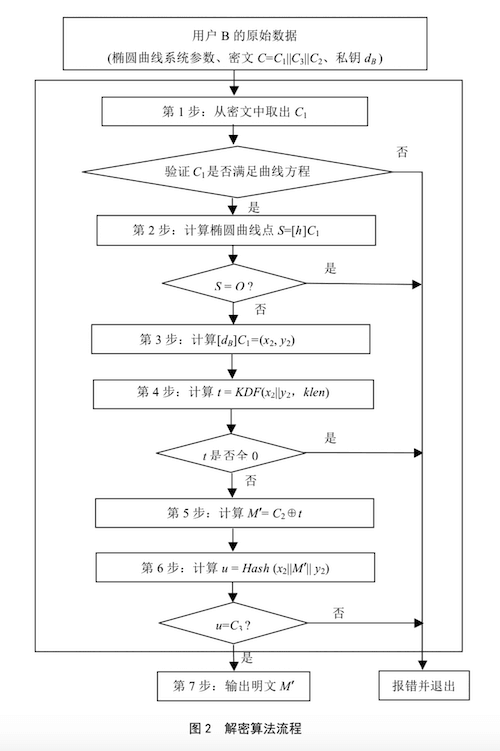
SM2 decryption is to go through the reverse process. Note that OpenSSL decryption requires the incoming ciphertext to be ASN1 encoded.
Suppose the elliptic curve is the recommended curve, the private key is d, the ciphertext is C (
- Take the bit string C1 (the first 64 bytes of the ciphertext C) from C, convert the data type of C1 to a point on the elliptic curve, and verify whether C1 satisfies the elliptic curve equation. If not, report an error and exit;
- Calculate the elliptic curve point
. If S is a point at infinity, report an error and exit; - Calculate
, and convert the data types of coordinates x2 and y2 to bit strings; - Calculate
. If t is a bit string of all 0s, report an error and exit; - Take the bit string C2 from C, and calculate
; - Calculate
, and take the bit string C3 (the last 32 bytes of the ciphertext C) from C. If , then report an error and exit; - Output the plaintext M', M' is the decrypted plaintext.